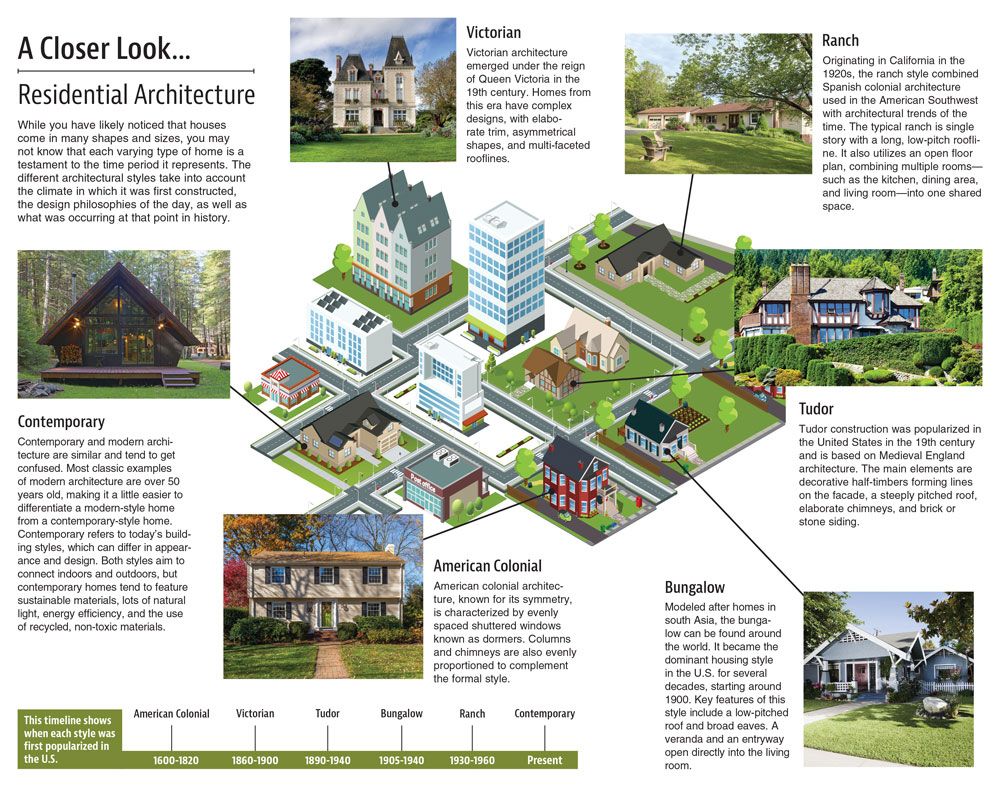
While you have likely noticed that houses come in many shapes and sizes, you may not know that each varying type of home is a testament to the time period it represents. The different architectural styles take into account the climate in which it was first constructed, the design philosophies of the day, as well as what was occurring at that point in history.
American Colonial
American colonial architecture, known for its symmetry, is characterized by evenly spaced shuttered windows known as dormers. Columns and chimneys are also evenly proportioned to complement the formal style.
Victorian
Victorian architecture emerged under the reign of Queen Victoria in the 19th century. Homes from this era have complex designs, with elaborate trim, asymmetrical shapes, and multi-faceted rooflines.
Tudor
Tudor construction was popularized in the United States in the 19th century and is based on Medieval England architecture. The main elements are decorative half-timbers forming lines on the facade, a steeply pitched roof, elaborate chimneys, and brick or stone siding.
Bungalow
Modeled after homes in south Asia, the bungalow can be found around the world. It became the dominant housing style in the U.S. for several decades, starting around 1900. Key features of this style include a low-pitched roof and broad eaves. A veranda and an entryway open directly into the living room.
Ranch
Originating in California in the 1920s, the ranch style combined Spanish colonial architecture used in the American Southwest with architectural trends of the time. The typical ranch is single story with a long, low-pitch roofline. It also utilizes an open floor plan, combining multiple rooms—such as the kitchen, dining area, and living room—into one shared space.
Contemporary
Contemporary and modern architecture are similar and tend to get confused. Most classic examples of modern architecture are over 50 years old, making it a little easier to differentiate a modern-style home from a contemporary-style home. Contemporary refers to today’s building styles, which can differ in appearance and design. Both styles aim to connect indoors and outdoors, but contemporary homes tend to feature sustainable materials, lots of natural light, energy efficiency, and the use of recycled, non-toxic materials.