 CDC/James Archer
CDC/James Archer
World News Desk
Learn the why behind the headlines.
Subscribe to the Real Truth for FREE news and analysis.
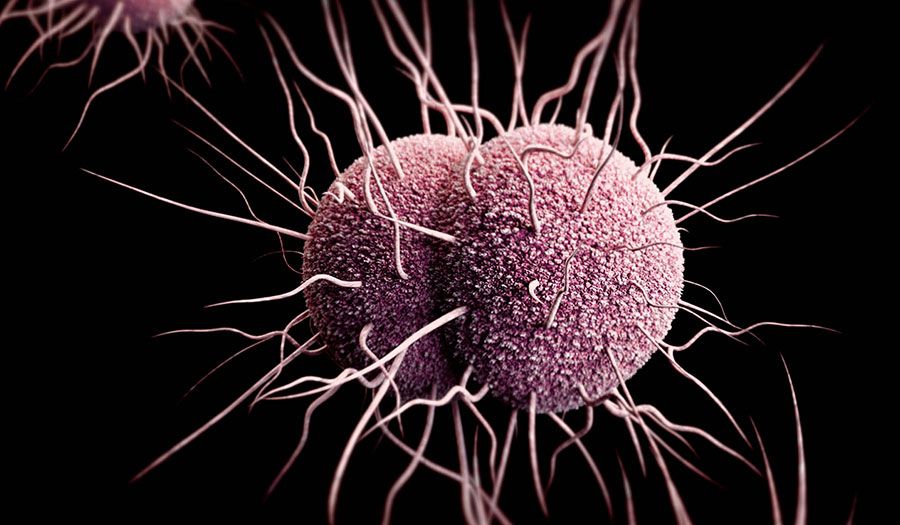
Subscribe NowNew cases of three common sexually transmitted diseases in the United States—chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis—reached an all-time high of 2 million in 2016, according to an annual report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released September 26. This is the third straight year the center reported increases in STD cases among Americans.
According to the report, since 2015, new cases of chlamydia have increased 4.7 percent to nearly 1.6 million. In addition, new cases of gonorrhea were up 18.5 percent to nearly a half million and cases of syphilis increased 17.6 percent to 27,814.
Most instances—80.6 percent—of syphilis occurred in men who had sexual encounters with other men, however, rates among women and newborns rose 36 percent and 28 percent, respectively.
Gail Bolan, director of the CDC’s Division of STD Preventions, stated on the national health institute’s website that the increasing prevalence of syphilis among newborns “represents a tragic systems failure.”
In a press release on its website, the CDC said that the report’s “trends are particularly alarming in light of the growing threat of drug resistance to the last remaining recommended gonorrhea treatment.”
While the effects of STDs are not always immediate, they can cause significant health problems such as infertility, infant stillbirth, and result in a greater risk of HIV transmission.
“Increases in STDs are a clear warning of a growing threat,” Dr. Jonathan Mermin, director of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, stated in the release. “STDs are a persistent enemy, growing in number, and outpacing our ability to respond.”


